mhc class ii function
Thus it causes the initiation of the immune response which is specific to the antigen. MHC class II molecules are transmembrane glycoprotein heterodimers constructed from α and β chains the genes for which are on the short arm of chromosome 6.

Major Histocompatibility Complex Mhc Faunafondness Antigen Presenting Cell Cell Membrane Heat Shock Protein
Activates B cells for antibody production.

. The presence of post-translational regulation of MHC class II MHC II under physiological conditions has been demonstrated recently in dendritic cells DCs that potently function as antigen-presenting cells APCs. The major histocompatibility complex MHC is a group of genes that encode proteins on the cell surface that have an important role in immune response. MHC class I molecules are one of two primary classes of major histocompatibility complex MHC molecules the other being MHC class II and are found on the cell surface of all nucleated cells in the bodies of vertebrates.
Major histocompatibility complex MHC class II molecules go to extraordinary lengths to make sure that they bind to peptides generated in the endosomallysosomal system reviewed byCresswell 1994. The function of MHC Class I protein is to expose the protein that lies within the cell to cytotoxic T-cells. They also occur on platelets but not on red blood cellsTheir function is to display peptide fragments of proteins from within the cell to cytotoxic T cells.
MHC-A MHC-B and MHC-C. The expression of MHC II molecules on thymic epithelial cells. It explains how MHC class 1 and 2 are processed.
Specific MHC class II alleles are. Antigens presented by MHC class I molecules are of endogenous origin. Abnormal Treg cell homeostasis and function did not reflect the involvement of p56Lck in CD4 function because these effects were not observed when CD4 expression was inactivated by Ox40-creThe results make clear multiple aspects of Treg cell homeostasis and phenotype that are dependent on a sustained capacity to signal through the TCR.
Helps immune system in recognising self-cells from non-self cells. Help Your Patients Improve Their Functional Class. MHC Class I There are three.
Functions of MHC class II proteins. The enzymes that are responsible for generating peptides are cytosolic proteasomes. MHC class II MHC-II molecules are present on antigen presenting cells APCs and these molecules function by binding antigenic peptides and presenting these peptides to antigen-specific CD4 T cells.
APCs continuously generate and degrade MHC-II molecules and ubiquitination of MHC-II has recently been shown to be a key regulator of MHC-II expression in. MHC class II molecules assemble in the endoplasmic reticulum in a chaperone-mediated fashion to form a nine-chain structure consisting of three alpha beta dimers associated with an invariant chain trimer. MHC Class II They consist of 2 alpha and beta domains.
The origin of the antigen that is presented by the MHC class I molecules is endogenous. Functions of mhc class ii. The antigens that are presented by the MHC class II molecules come from an extracellular source.
There are 3 different human MHC-II isotypes HLA-DR -DP and -DQ encoded by distinct α chain A and β chain B genes that are. Here we report that MARCH-I an E3 ubiquitin ligase plays a pivotal role in the post-translational regulation of MHC II in B cells. MHC Class I Their main role is to clear endogenous antigens.
Ad Learn How Functional Class Changes Can Influence Patients Risk Status. Ad Pioneer of Recombinant Antibody DiscoveryManufactureQuality ControlFind Your Antibody. Newly synthesized MHC class II alpha and beta chains associate with a protein chaperone the invariant chain which promotes the proper assembly of MHC class II complexes and their trafficking through cells and prevents their untimely loading with peptides.
MHC Class II proteins are encoded by the genes of the HLA-D region. CD4T-cells are specific for MHC-II. Key Difference MHC I vs II In the context of immunity Major Histocompatibility Complex MHC is an important molecule during the recognition of antigens foreign substances.
Basic immunology notes CD4 chromosome 6 Functions of MHC class 2 glycoproteins HLA-D loci immunology notes mhc class 1. Mhcs are essential for adaptive immunity. MHC class II molecules offer exogenous peptides to CD4 T-lymphocyte receptors to commence the normal adaptive response.
MHC class I proteins are encoded by the HLA-A HLA-B and HLA-C genes. MHC-II plays a significant role in graft versus host response and in mixed lymphocyte reaction. Antigens presented by MHC class II molecules are derived from extracellular proteins.
Helper T cells recognises antigens bound to MHC Class II proteins. Aim For Low Risk. The presence of post-translational regulation of MHC class II MHC II under physiological conditions has been demonstrated recently in dendritic cells DCs that potently function as antigen-presenting cells APCs.
4 6 and 9 Encoded genes. Responsible for rejection of transplanted organs. PAH Initiative Has Resources Available.
Here we report that MARCH-I an E3 ubiquitin ligase plays a pivotal role in the post-translational regulation of MHC II in B cells. MHC-II molecules also called human leukocyte antigens HLA in humans are heterodimeric transmembrane glycoproteins consisting of α and β chains. MHC class 1 and 2 - This immunology lecture explains about the structure and functions of MHC class 1 and 2.
They are considered to be a set of cell surface proteins which basically function to bind with foreign antigens to present them on either of the T cell types. Functions of Major Histocompatibility Complex II. The signal for endosomal targeting resides in the cytoplasmic tail of the invariant.
This study investigated the underlying mechanism of antigen assembly and the HBV antigen-presenting function of major histocompatibility complex MHC class I molecules using heat shock protein gp96. The main function of the MHC class II protein is to present the processed antigen that basically comes from the exogenous source to T-lymphocytes CD4. High Quality Product from Research to Scale-up Quantities.
First in the endoplasmic reticulum ER newly synthesized class II α and β chains associate with the invariant Ii chain to form a complex that itself is incapable. Major function of MHC-II is to bind peptide antigen and present to CD4 T cells. Functions of MHC class II.
MHC Class II MHC-D. MHC class II engagement is crucial to the induction and regulation of adaptive immunity by selecting the mature CD4 T cell repertoire in the thymus and activating these lymphocytes in the periphery. A mhc class i b mhc class ii c mhc class iii d all of the above 6 the mhc molecules are encoded by specific genes.
First western blotting flow cytometry co-immunoprecipitation GST pull-down and confocal microscopic assays were performed to. Endosomal proteolysis and MHC class II function Curr Opin Immunol. T helper cells T H or cytotoxic T.
Structure Function and Regulation of MHC Class II Molecules. The major function of the class i gene product is presentation of peptide antigens to tc cells. MHC Class II Their main role is to clear exogenous antigens.
MHC-II are found on surface of Antigen presenting cells APCs. This complex is transported through the Golgi apparatus and into the endosomal system.

Antiviral Effects Of Interferon Antiviral Biochemical Diffuser

Mhc Class 1 Vs 2 Google Search Physiology Human Anatomy And Physiology Biomedical Science

Antigen Recognition By Effector T Cells Antigen Presenting Cell B Cell Anatomy And Physiology

Pin On Immunologie Und Erkrankungen Des Immunsystems

Complement Pathways Types Functions And Regulation Medical School Studying Studying Medicine Medical Laboratory Science

Antigen Presenting Cells Phagocytize An Antigen And Uses A Lysosome To Degrade It Into Smaller Piec Medical Laboratory Science Medical Studies Teaching Biology

Mhc Class Ii Structure And Function Biology Exams 4 U Structure And Function Plasma Membrane Immunology
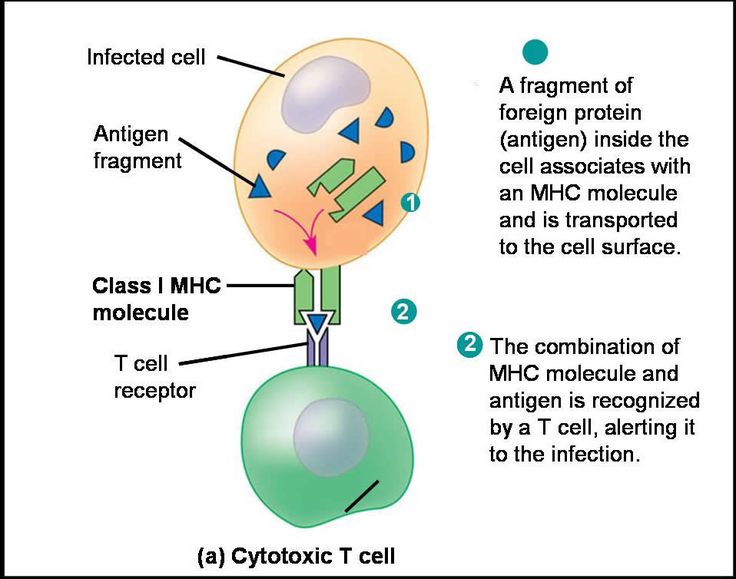
Associate Degree Nursing Physiology Review

Mhc Class 1 Vs 2 Google Search Physiology Human Anatomy And Physiology Biomedical Science

T Cell Receptors Overview Mini Review Bio Rad

Difference Between Mhc Class I And Mhc Class Ii

Major Histocompatibility Complex Mhc Class 1 Displays Reproduced Antigens In Infected Or Cancerous Cells Class 2 Immunnaya Sistema Gematologiya Biohimiya

B Cells As Antigen Presenting Cells Or Apcs Mechanism

An Experimental Animal Model For Central Nervous System Demyelinating Disease Inoculation With A White Matter Emu Immunology Demyelinating Disease Autoimmune

B Cell Activation Medical School Studying Immunology Medical Technology

Processing Af Extracellular Antigen For Class Ii Mhc Presentation Follows A Different Pathway


